Rally Combines the Power of Many Tools to Deliver One Powerful Benchmarking Wizard
Mirantis is pleased to announce the upcoming release of the new OpenStack benchmarking tool--Rally. Rally is responsible for deploying OpenStack on a given cloud configuration, testing this deployment for correctness, as well as for carrying out various performance measurements.
Why Rally
OpenStack is an extremely complicated and flexible piece of software that consists of many subsystems and components. As a result, when trying to test and to understand how different implementation decisions and changes proposed to OpenStack affect the whole system’s behavior and performance, OpenStack integrators and developers inevitably face the problem of dealing with its immense complexity. Moreover, the great variety of possible cloud configurations where OpenStack can be installed and used makes the task of conducting benchmarks even more difficult.
The fact is that it is barely possible to get relevant results when testing and benchmarking only local parts of OpenStack. On the contrary, launching specific benchmarking procedures on a prepared installation of the whole OpenStack system, using a predefined cloud configuration, would give much more positive and practically useful results. That is exactly what Rally is intended for: this project provides the community with a cloud benchmarking tool capable of performing specific complicated and reproducible benchmark scenarios on real OpenStack deployments.
Inside Rally
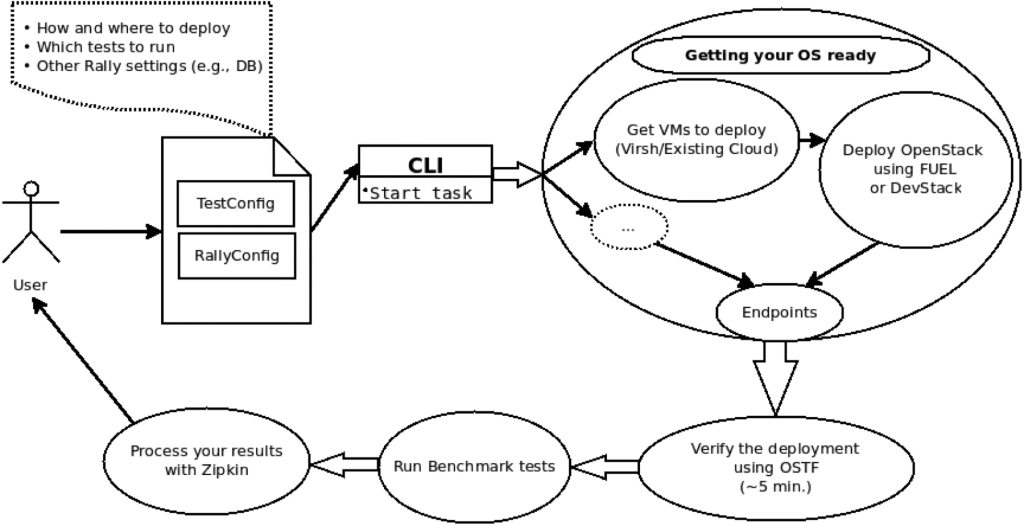
Rally communicates with OpenStack through the OpenStack API. It automatically installs and tests OpenStack, sends reports to a database, and performs data profiling, creating a dedicated page with an installation image. After it’s done with the work, Rally cleans up the installation.
Rally compiles a number of existing benchmarking facilities into one project, which makes it flexible to user requirements and ensures the reproducibility of test results. It consists of four components:
- Deploy Engine, which is responsible for processing and deploying VM images (using DevStack or FUEL according to the user’s preferences). The engine can do one of the following:
- Deploy an OS on already existing VMs.
- Start VMs from a VM image with pre-installed OS and OpenStack.
- Deploy multiple VMs inside each has OpenStack compute node based on a VM image.
- VM Provider, which interacts with cloud provider-specific interfaces to load and destroy VM images.
- Benchmarking Tool, which carries out the benchmarking process in several stages. It:
- Runs Tempest tests, reduced to 5-minute length.
- Runs the user-defined test scenarios (using the Rally testing framework).
- Collects all the test results and processes them by Zipkin tracer.
- Puts together a benchmarking report and stores it on the machine Rally was launched on.
- Orchestrator, which is the central component of the system. It uses the Deploy Engine to run control and compute nodes and to launch an OpenStack distribution and, after that, calls the Benchmarking Tool to start the benchmarking process.
Here’s a diagram of Rally in action.
The profiling is performed to establish how OpenStack works--how many users thousands of servers can support. Rally fires up the virtual machine, performs a request on it, and then shuts it down, showing how the install affects the speed and quantity of requests. Rally detects scale and performance issues, and helps show you what is slowing your cloud. You can use this info to fix those causes, and then iterate with the same benchmark tests to ensure that the changes you made actually improved performance.
Ultimately, when the users complete the installation, they know how many users they will have and what they will need to do to make OpenStack work.
For more information about the tool, please visit the Rally wiki page.
About Boris
Boris is a Technical Lead of the OpenStack Community group at Mirantis. He coordinates the work on various OpenStack projects and the OpenStack benchmark system. Also, he is a just another OpenStack contributor.